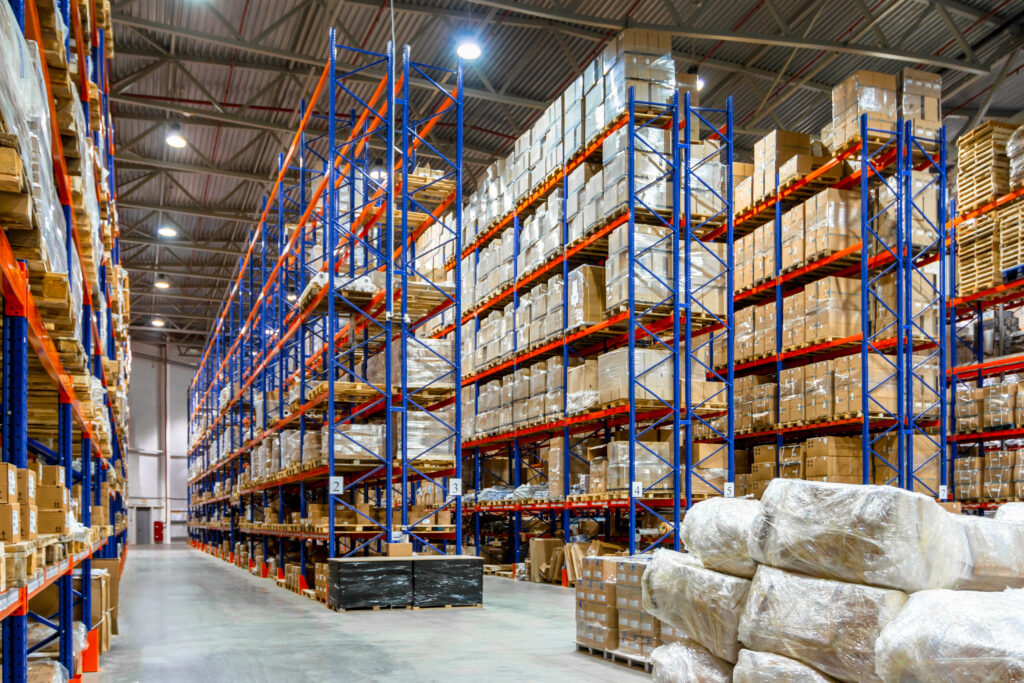
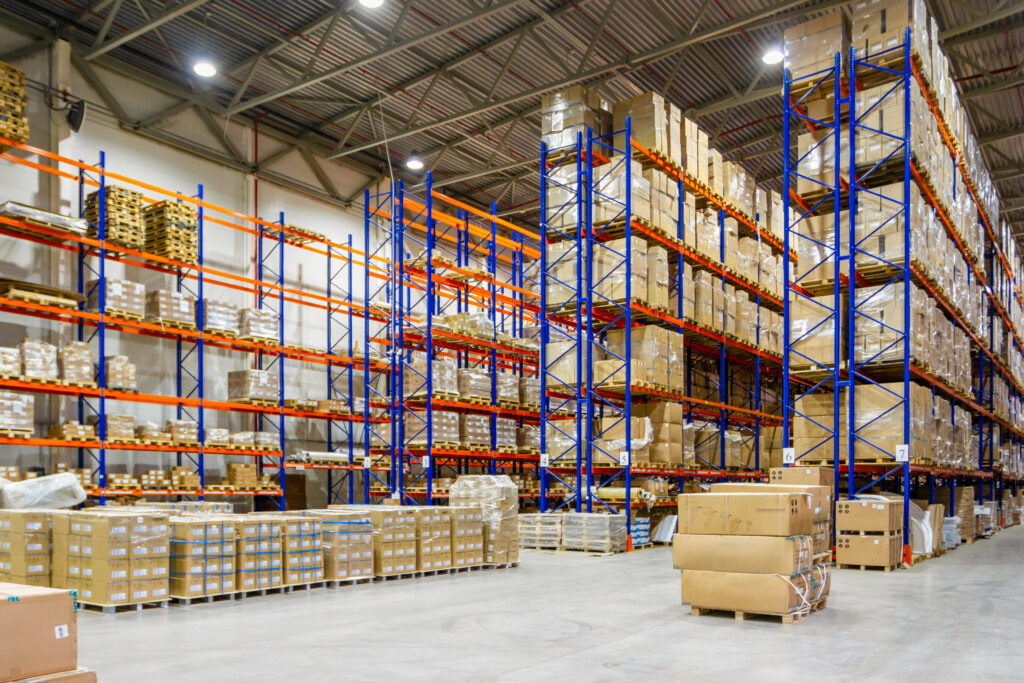
Selective Pallet Racking Systems in Portland, Oregon
Selective pallet racking systems meet all pallet standards worldwide, including the most popular standard developed by the
Grocery Manufacturers Association (GMA).
At Lenokers, we provide and install these systems for warehouses across the Portland metropolitan area and throughout Oregon.
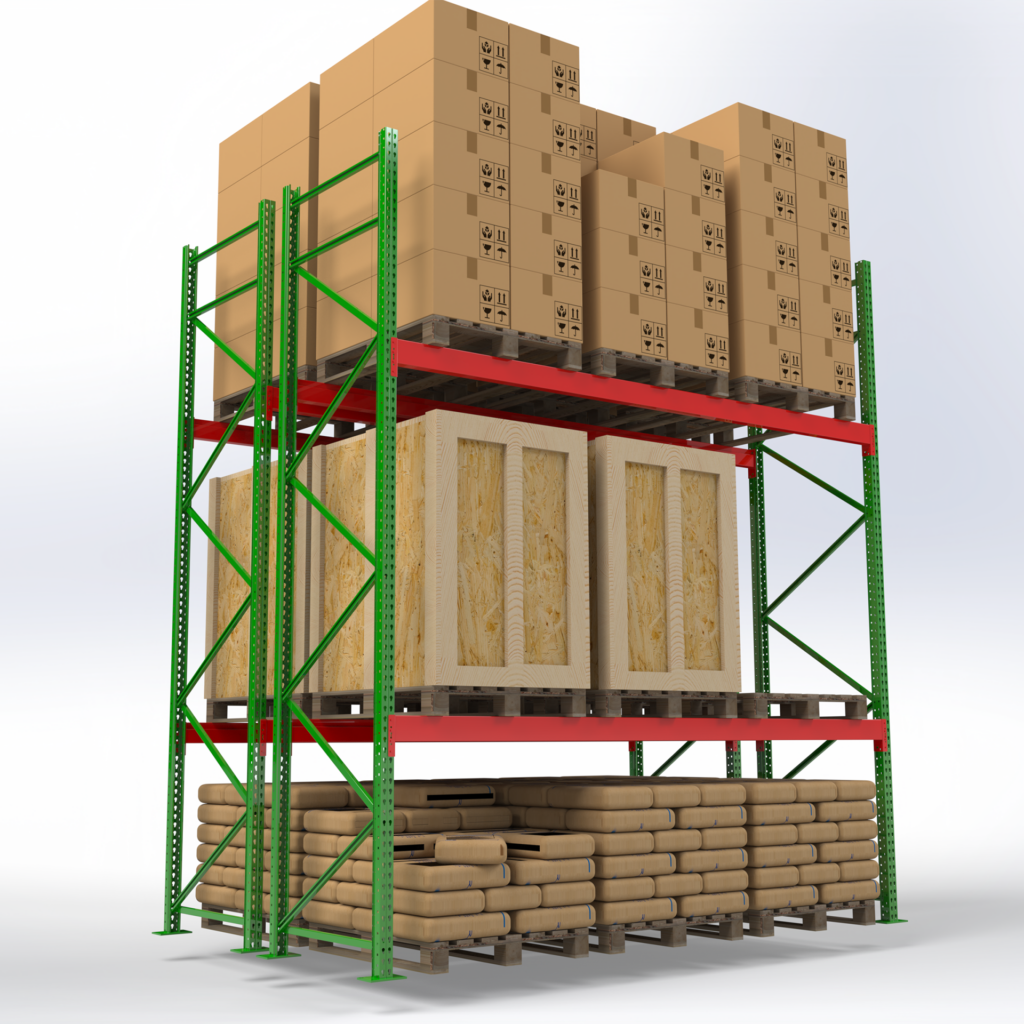
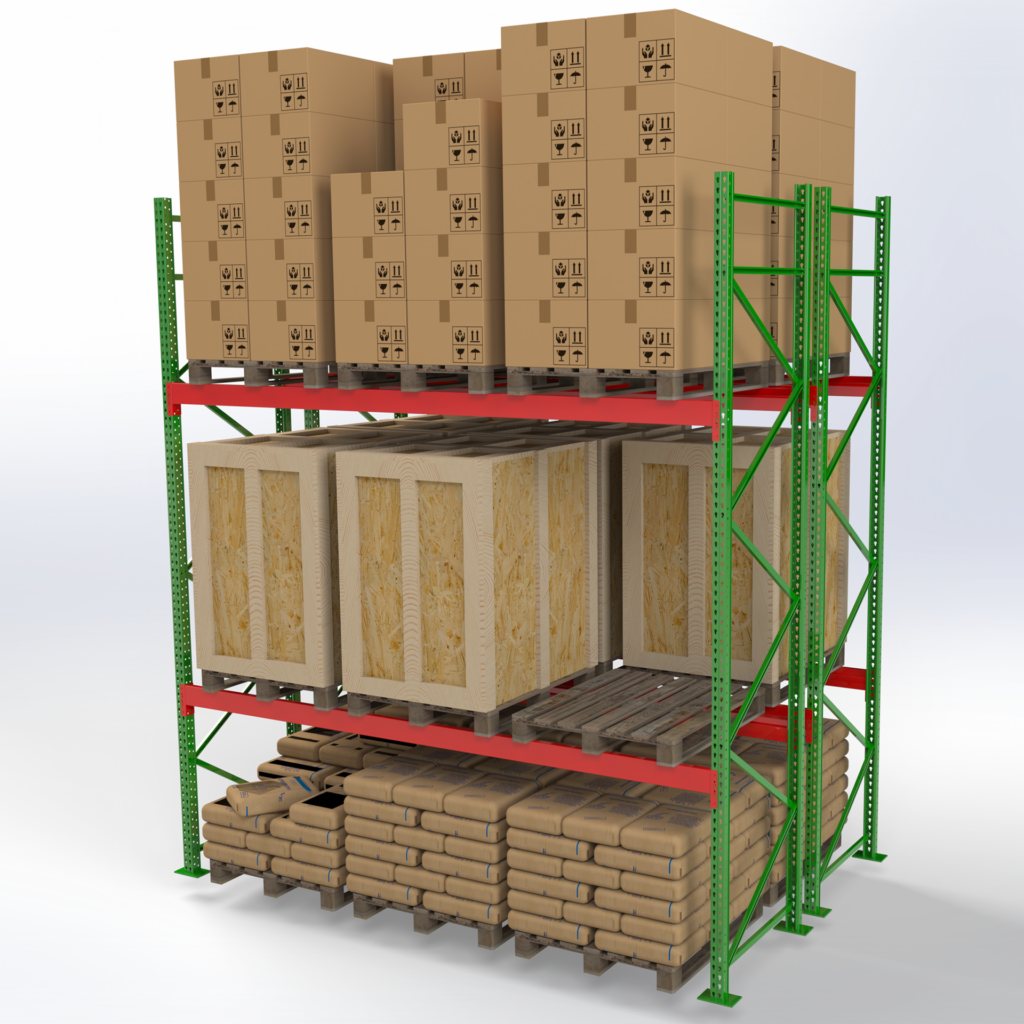
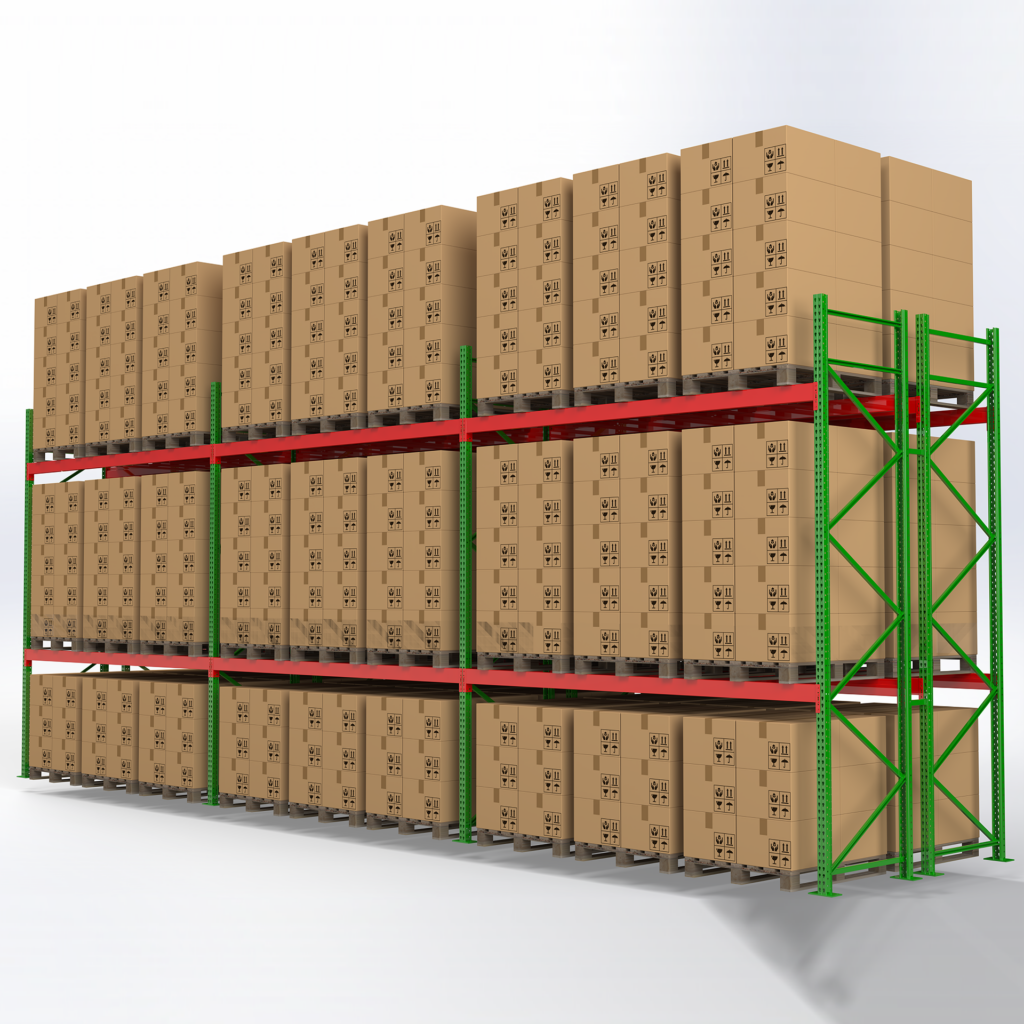
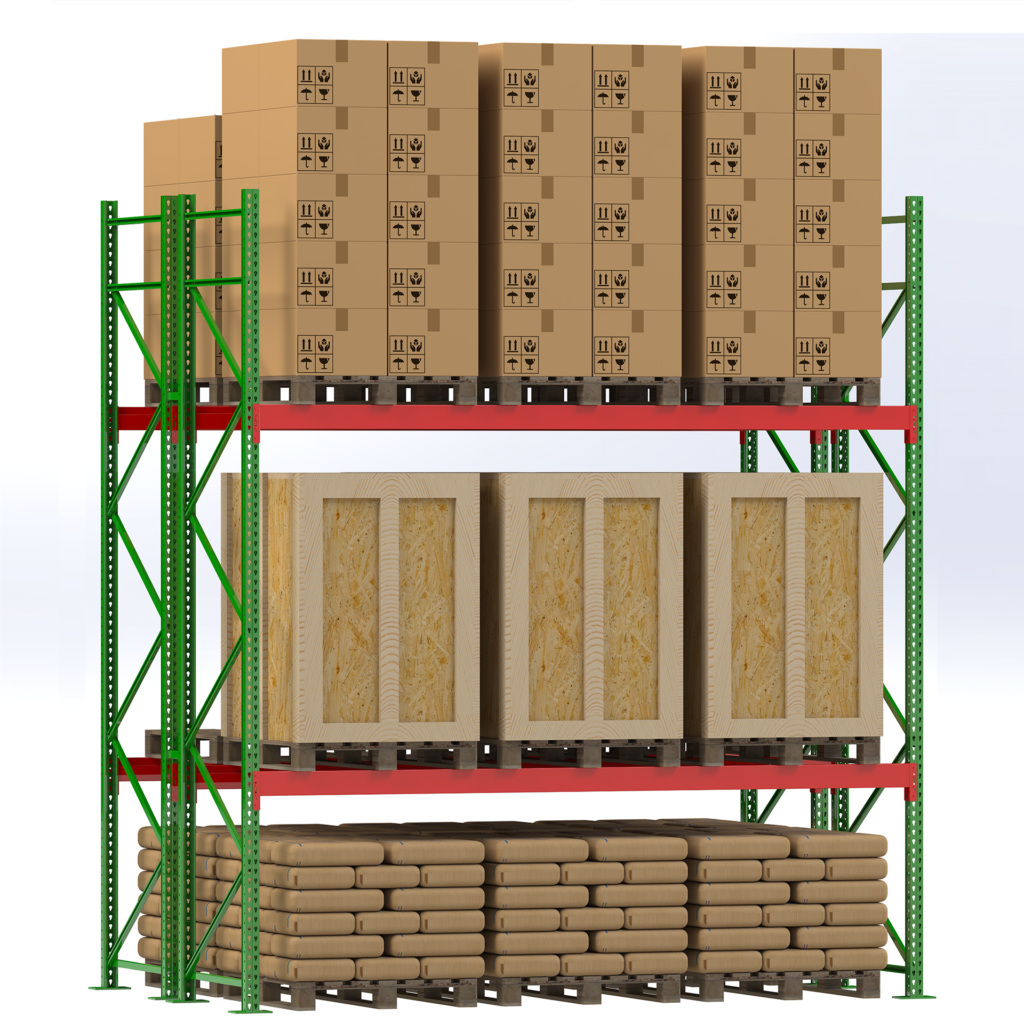
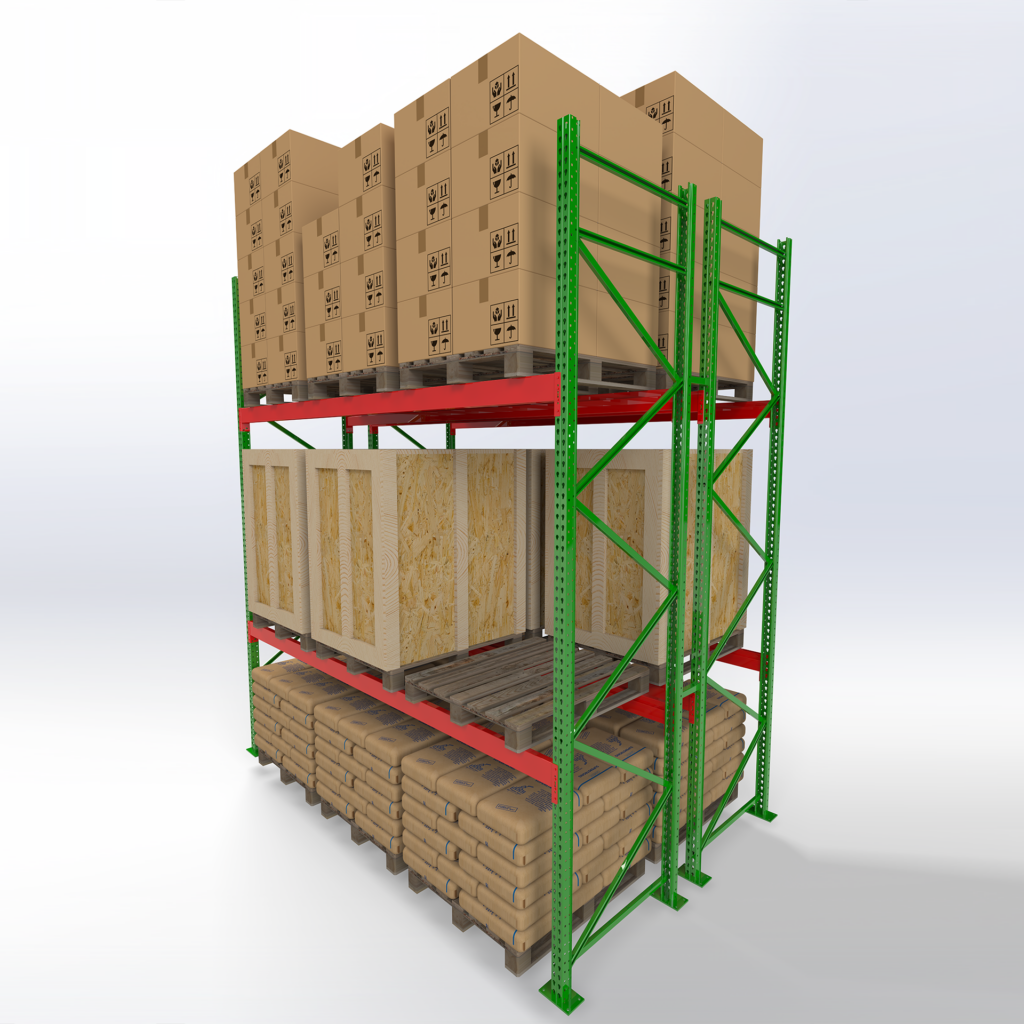
Types of Selective Pallet Racks
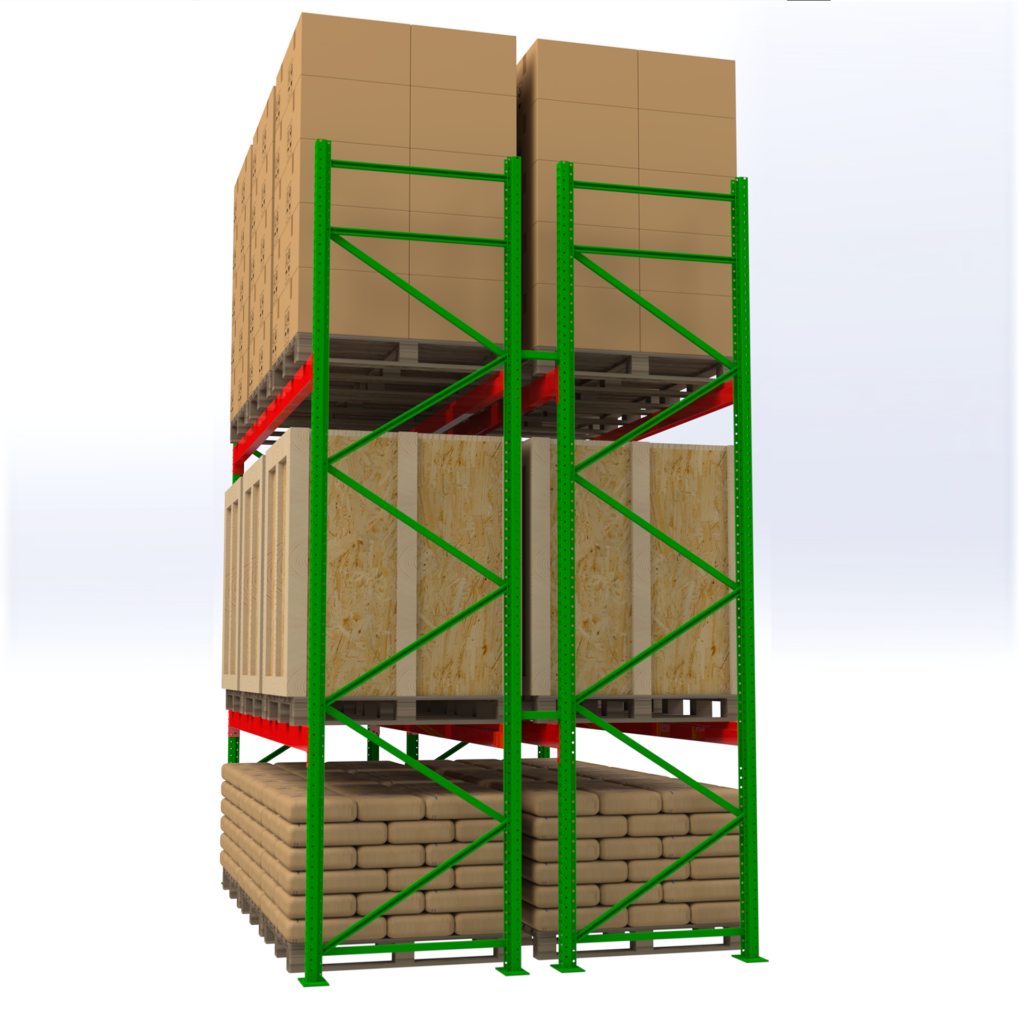
Roll-Formed Selective Racks
Main components: upright frames + horizontal beams (decks optional to create shelves).
Frames available with kant-leg or step-back leg base.
Open-column design, available in 3” or 4” wide sections.
Accessories include row spacers, wall ties, crossbars, and column guards.
Step Beams
Attached to vertical frames.
Manufactured with three- or four-pin connectors, allowing 2” vertical adjustability.
Available in various profile heights with bolted end connectors for structural channel frames.
Structural Steel Selective Racks
A durable solution for high-capacity and high-abuse warehouse operations.
Channel beams with two-bolt, four-hole x 8” connectors, also with 2” adjustability.
Frames available in straight, steep ascent, or caged units.
No field welding required.
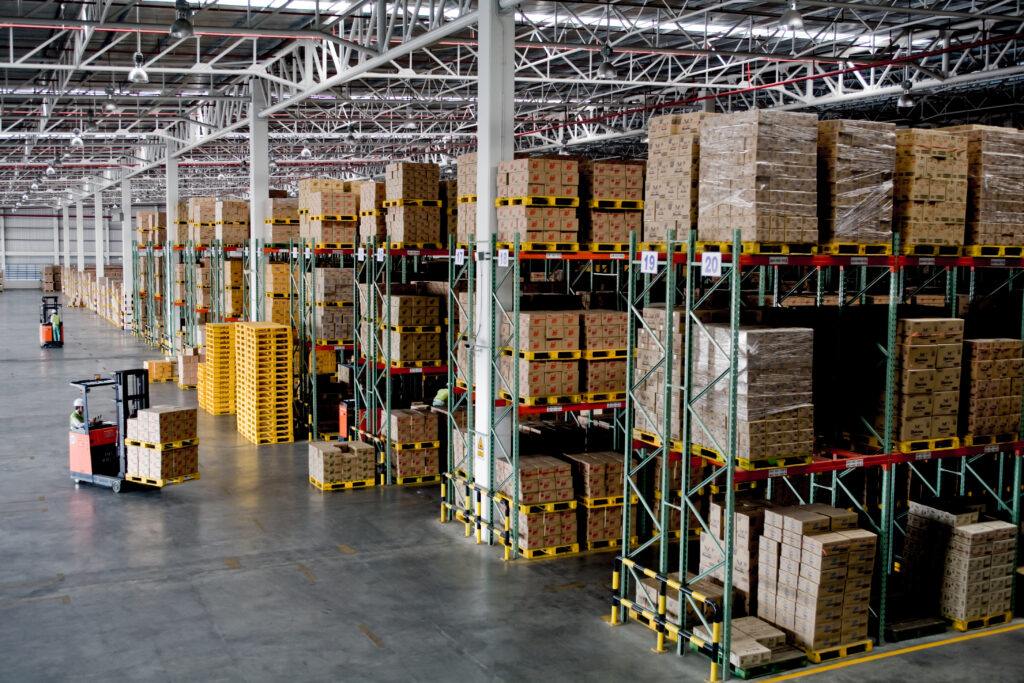
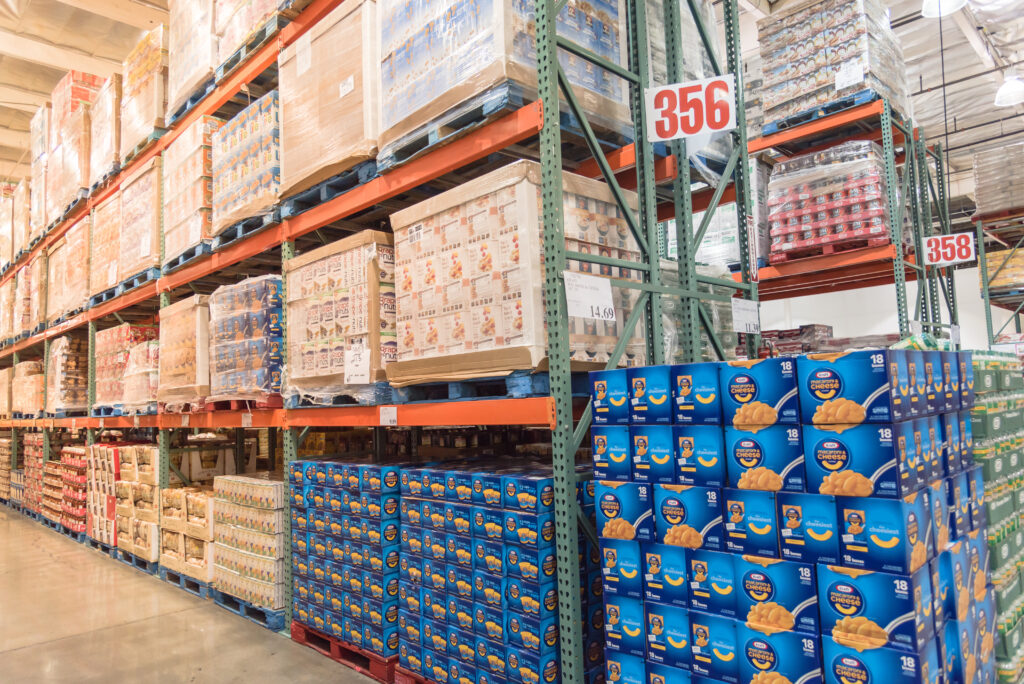
Benefits of Selective Pallet Racks
Lower cost and faster installation compared to other racking systems.
Easy access to any pallet at any time.
Option for double-depth racks to place pallets back-to-back.
Supports multiple inventory systems: FIFO, LIFO, or a mix.
Storage utilization around 45%, depending on warehouse conditions and OSHA requirements.
First level can serve as a picking area.
Can be integrated with conveyor systems.
Why Work With Lenokers?
Lenokers has decades of experience installing and dismantling pallet racking systems worldwide. We know every detail about these solutions and can provide exactly what your warehouse needs.
📞 Contact us today — we’ll make sure you get the right system, built for your requirements.